| • |
Use a standardized tool when screening for depression (e.g., the Patient Heath Questionnaire (PHQ-9)
or ASK-20 Survey). |
| • |
When assessing a patient with depression, assess for level of severity
and distinguish between single-episode depression versus recurrent
depression; document this information in the patient’s record. |
| • |
Use screening and motivational interviewing to assess patient self-efficacy
when prescribing a new antidepressant medication. Use results to
facilitate discussion around patient concerns and address challenges
that he/she feels might be barriers to medication adherence. |
| • | Obtain and document all available medication and other treatment response history. |
| • | Provide education to the patient regarding potential side effects of
antidepressant medication, and encourage the patient to secure a
relational support system during the treatment period. |
| • | Establish a protocol for following up with the patient, providing the
opportunity to communicate with you regarding his or her experience
taking the medication and the onset of any side effects if applicable. |
| • | Complete a Release of Information Authorization form, so that communication
can occur between the patient’s primary care clinician and behavioral
health provider. |
| • | Ensure integration of care by establishing a communication pathway
between the patient’s primary care clinician and behavioral health
provider. |
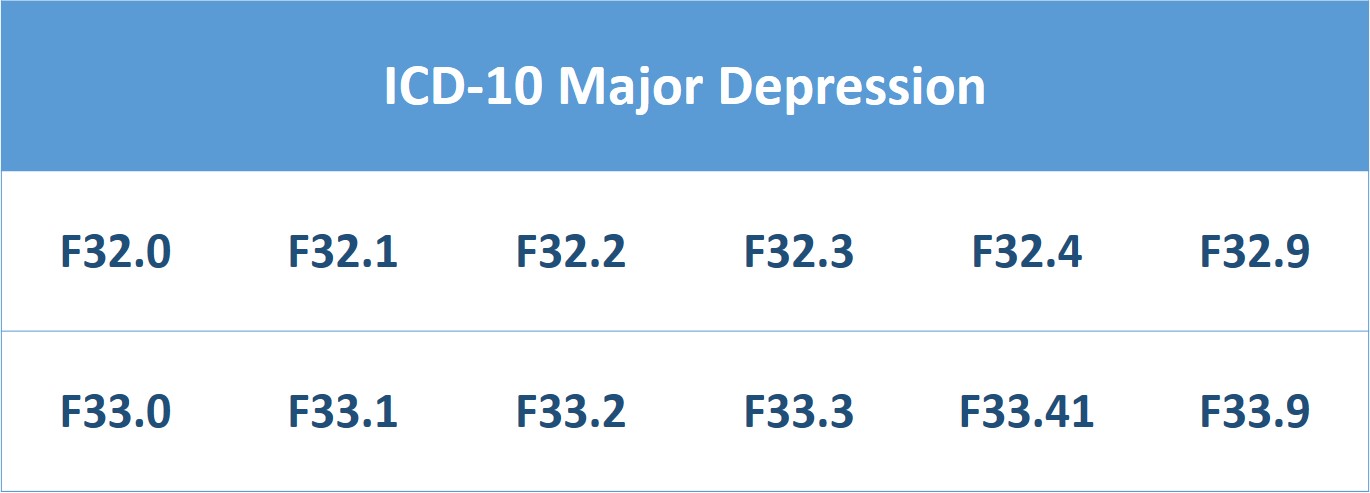
| • |
Utilize the diagnosis codes for major depression when filing claims (see below for a list of codes). |